Brain Abscess
The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
Brain abscess is as an intracranial space-occupying lesion that develops from a infection in the brain (initially a cerebritis), which is commonly an infection of the ear, nose or tooth, but may be a complication of a systemic infection, or result from infection introduced intracranially by trauma or surgical procedures. Empyema or meningitis may be preceding conditions.
It is most commonly caused by pyogenic organisms such as streptococci, staphylococci, and anaerobes. Gram negatives are an important cause in infants, including organism such as Citrobacter, Proteus, Serratia.
Pathologically, the infection process is focal, resulting in cerebritis, with edema, scattered necrosis and petechial hemorrhages. Eventually, as the infection becomes more focal, more necrosis ensues, which is followed by a capsule formation rich in collagen. The abscesses tend to occur in the corticomedullary junction of the frontal and parietal lobes.
Clinically, patients have symptoms of both systemic inflammation and focal symptoms from neural compression and intracranial hypertension – fever, headaches, vomiting, confusion, hemiparesis. If sufficiently large, it can complicate in cavernous sinus thrombosis, or brain herniation.
CT scan shows an area of contrast enhancement surrounding a hypodense core, which have similar appearance to metastatic neoplasms. The early stages can be seen in MRI, due to the presence of edema and scattered necrosis, which changes increases the signal in T2. As in meningitis, imaging prior to lumbar puncture is crucial to determine risk of brain herniation when there is mass effect. However, examination of the cerebrospinal fluid does not help in diagnosis.
Left untreated, it carries a very high mortality rate. Treatment consists of antibiotic therapy. It has a significant long-term morbidity.
|
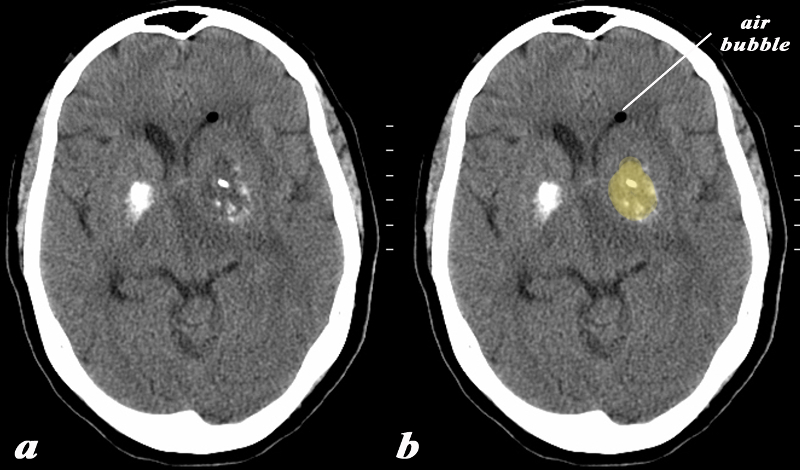
Calcification and Mass in the Basal Ganglia on the left Evolving Abscess |
|
The basal ganglia in the region of the caudate nucleus and globus pallidus are shown in axial projection in this 60 year old female who presents with neurological deficit and a fever. The CT scan shows asymmetric calcification in the region of the caudate nucleus and globus pallidus. The calcifications on the left are expanded by a low density presumably fluid collection (yellow). There is associated surrounding edema and mass effect on the ipsilateral ventricle. A small air bubble is noted in the anterior most portion of the left frontal horn. There is mild midline shift An MRI confirmed the presence of a complex fluid in the left basal ganglion and significant surrounding edema. The patient had a fever and the constellation of findings were consistent with an abscess of the basal ganglia on the left. In this diagram the intimate relationship of the basal ganglia to the ventricles is exemplified by the ipsilateral mass effect and the presence of air presumably from gas forming organisms. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 89065c01.8 |
|
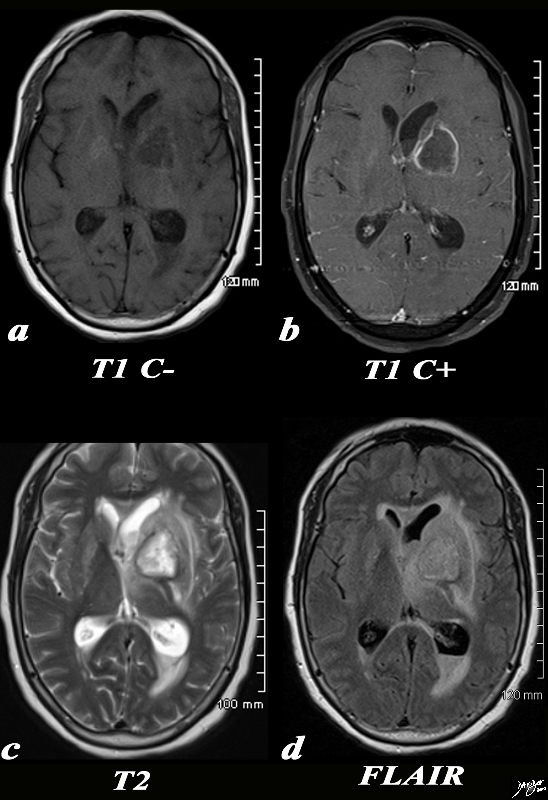
Abscess Left Basal Ganglia |
|
The basal ganglia in the region of the caudate nucleus and globus pallidus are shown in axial projection in this 60 year old female who presents with neurological deficit and a fever. In the first image the focal ill defined mass with mild mass effect is shown in axial projection on a T1 weighted image without contrast (a). The second image with gadolinium shows rim enhancement with mass effect and obstruction of the frontal horn as seen by asymmetric dilatation (b). The third T2 weighted image (c) shows the fluid nature of the cavity and the surrounding edema, mass effect, and accumulation of fluid in the dependant portion of the occipital horn. The fourth image is a FLAIR image and also shows th extent of the edema in the brain The patient had a fever and the constellation of findings were consistent with an abscess of the basal ganglia on the left. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 89054c.8s |

Right Frontal Abscess Secondary to Sinusitis |
|
The MRI is from a 40 year old female who presents with a headache and has maxillary sinusitis which was complicated by a brain abscess. Image (a) is a T1 weighted axial image taken at the level of the lateral ventricles and shows a mass with an air bubble and a small air fliouid level in the right frontal lobe. Image (b) is a T2 weighted image showing complex fluid in the abscess cavity that is not as intensely bright as the CSF. There is surrounding edema in the brain substance and the black air bubble is again seen. Image c is FLAIR sequence in axial projection that has features similar to the T2 weighted image and image (d) is a coronal FLAIR sequence showing the paracentral location of the abscess. In image (d) the right maxillary sinus is normal and air containing while the left maxillary sinu is is totally opacified consistent with the diagnosis of maxillary sinusitis Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 71604.c02 71604.c03 71604.c04 71604.c02 71604.c02b |