The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
The amygdala is part of the limbic system and is characterized by its role in memory and emotion.
The amygdala is a component of the limbic system with the basal ganglia, hippocampus, and septum. Structurally It is an almond shaped cluster of neurons in the anterior temporal lobes above the hippocampus. It is also in intimate contact with the caudate nucleus. It lies as a cluster of neurons above the hippocampus in the anterior temporal lobes of the brain It is separated into two nuclear regions. The amygdala receives input from the olfactory cortex, hypothalamus, and thalamus
The function of the amygdala is to aid in forming and maintaining memory, to regulate emotional responses and food intake, and to mediate reflex responses.
Common diseases involving the amygdala include certain psychological disorders, autism, and Alzheimer’s disease. Damage to the amygdala can inhibit conditioning and cause hyper-sexuality, agnosia, and loss of fear and aggression.
Commonly used diagnostic procedures for diseases of the amygdala include positron emission tomography, CT scans, and MRI scans.
Psychological diseases involving the amygdala are usually treated with serotonin reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic anti-depressants, benzodiazepines, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and glutamate. Hyperactivity of the amygdala is typically treated with glutamate.
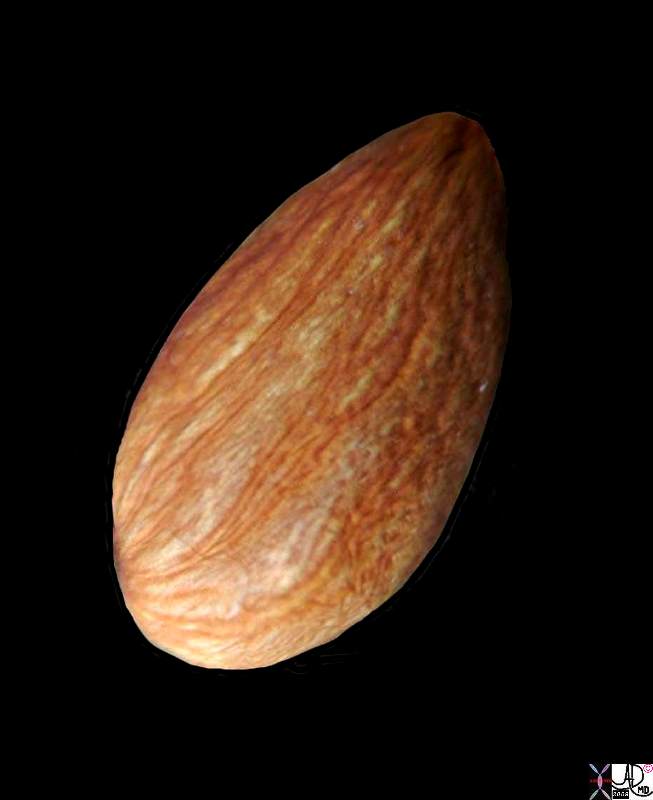

Amygdala = Almond The Shape of the Amygdala |
| Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2010 82470.81s |

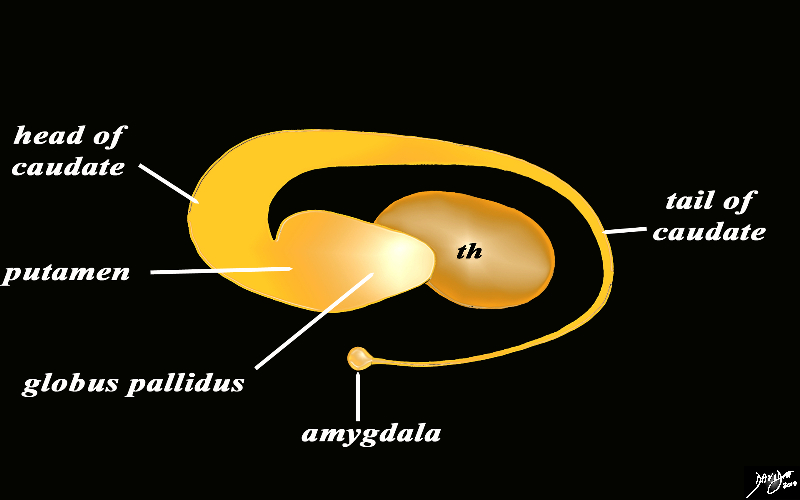
The Inner Orange C- Ring |
|
The orange c shaped ring lies lateral and to some extent inferior to the lateral ventricles typified by the light blue ring and consists of the thalamus and basal ganglia including the globus pallidus, putamen, head of the caudate nucleus, tail of the caudate nucleus and the amydala. This diagram infers the concept of recurring inverted C shaped structures that are layered both from deep to superficial but also to some extent medial to lateral. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 93907d13b05b02.8s |
|
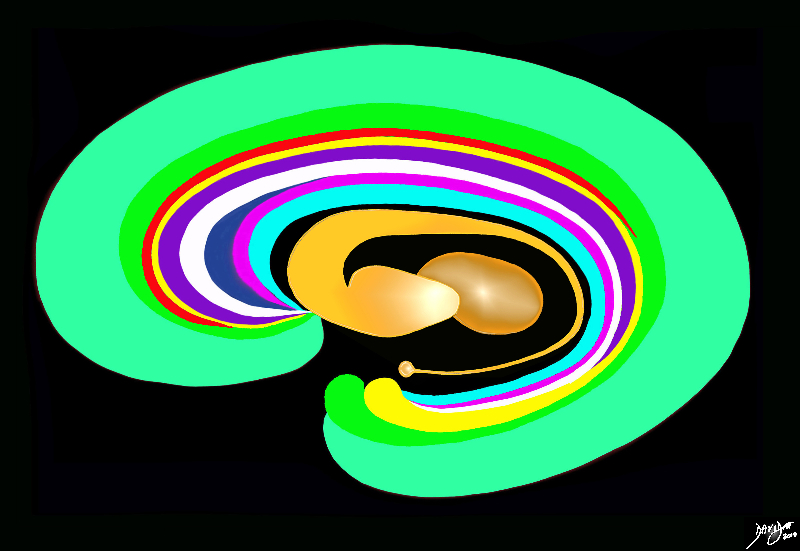
The Basal Ganglia of the Forebrain in Sagittal Projection |
|
The basal ganglia lie both in the forebrain and in the midbrain. In the forebrain they are distributed in paraventricular fashion almost in an inverted C fashion. In the conceptual diagrams we have colored the inverted “C” that abuts the ventricular system orange, and this includes the thalamus and the basal ganglia. The basal ganglia that lie in the forebrain include the globus pallidus, putamen, head of the caudate nucleus, tail of the caudate nucleus and the amygdala. The amygdala appears to be part of the limbic system and the basal ganglia. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 93907d13b05dL3.8s |
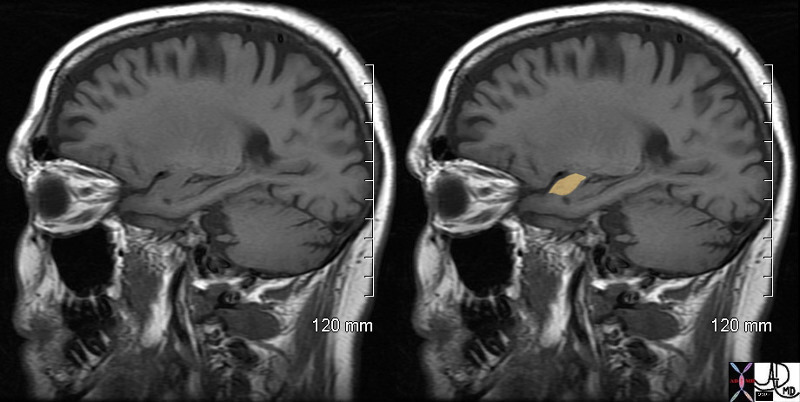
The Amygdala – T1 Weighted Sagittal Projection |
|
The T1 weighted MRI projection shows a normal brain with the amygdala highlighted in orange Courtesy AshleyDavidoff MD copyright 2010 72212c01 |
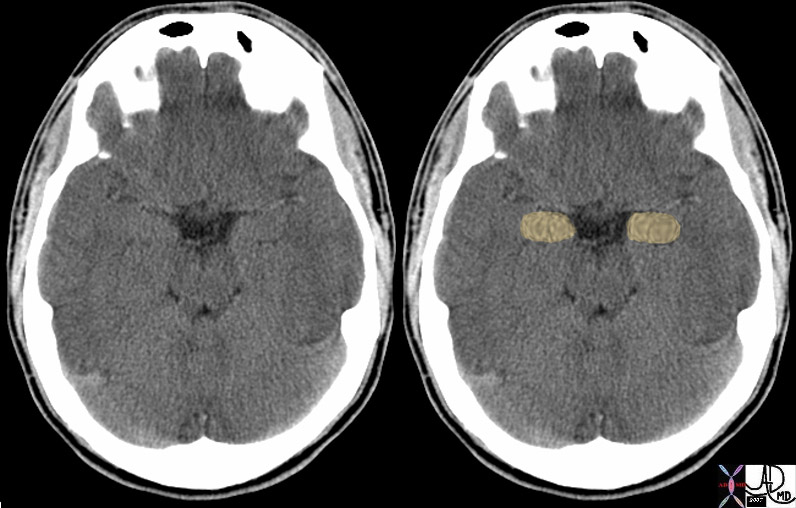
The Amygdala in Transverse Plane |
| 72120c01 brain cerebrum cerebral normal amygdala amygdaloid emotion shape almond normal anatomy Davidoff MD |
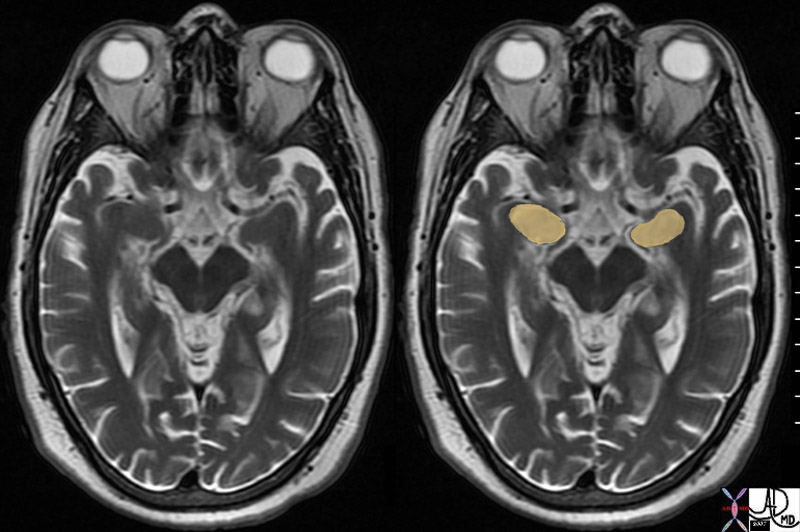
Amygdala T2 Weighted MRI Axial Plane |
|
brain cerebrum cerebral normal amygdala amygdaloid emotion shape almond normal anatomy MRI T2 weighting Davidoff MD 72195c01 |
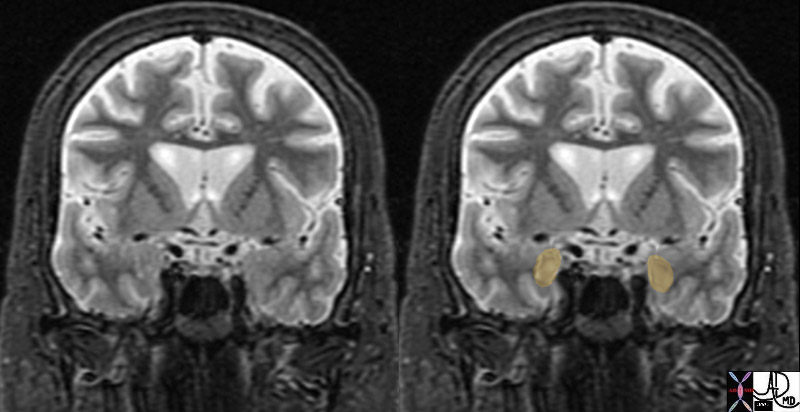
Normal Amygdala in the Coronal Plane STIR Images |
| brain cerebrum cerebral normal amygdala amygdaloid emotion shape almond normal anatomy MRI STIR coronal projection Davidoff MD 72233c01 |