The Common vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
Sagittal Plane
|
The Venous System – Concepts |
|
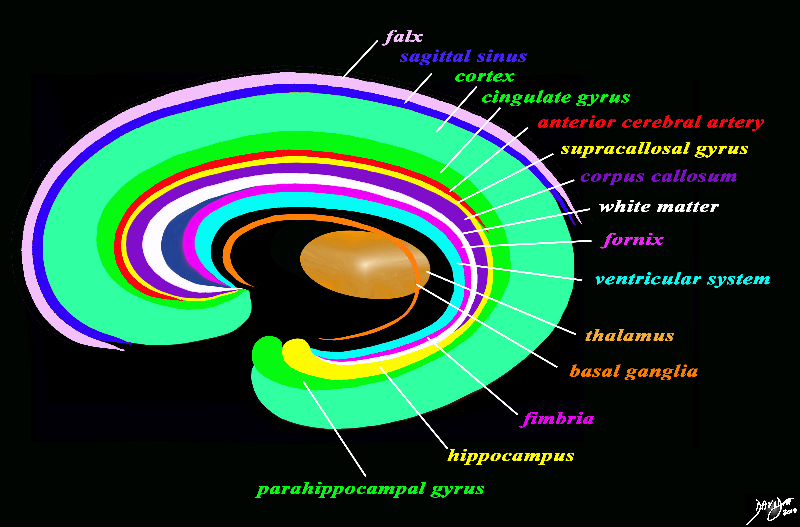
The forebrain has most of its components aligned in a series of inverted c- shaped rings starting from the outer membranes that culminate in the falx (pink), then extending inward smaller inner rings with each intimately connected to the others. The venous system follows this pattern in that the superior sagittal sinus and the inferior sagittal sinus both follow the inverted C concept. In this diagram the the “sagittal sinus” is conceptua;ised in relation to the falx The thalamus (dull orange) appears diagrammatically as the centre of these rings as seen from the sagittal view The outer ring is the falx (pink) followed by the sagittal sinus (blue) cerebral cortex (light green), cingulate gyrus (bright green) superiorly which becomes the parahippocampal gyrus inferiorly. The red ring represents the distribution of the main portion of the anterior cerebral artery. Next is the yellow ring which is the supracollosal gyrus (indusium griseum) superiorly and the hippocampus inferiorly. This is followed by the corpus callosum (purple) which enables the white ring of white matter to connect between hemispheres. The next ring is the thin bright pink ring which represents the fornix superiorly and the fimbria inferiorly. The innermost ring (light blue) represents the lateral horns of the ventricular system. The basal ganglia run just lateral to the lateral ventricles. The navy blue arrow headed structure is the septum pellucidum. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93907d13g03.8s |
Two Vertically Oriented ‘Inverted C’s” Superior sagittal Sinus and Inferior Sagittal Sinus |
|
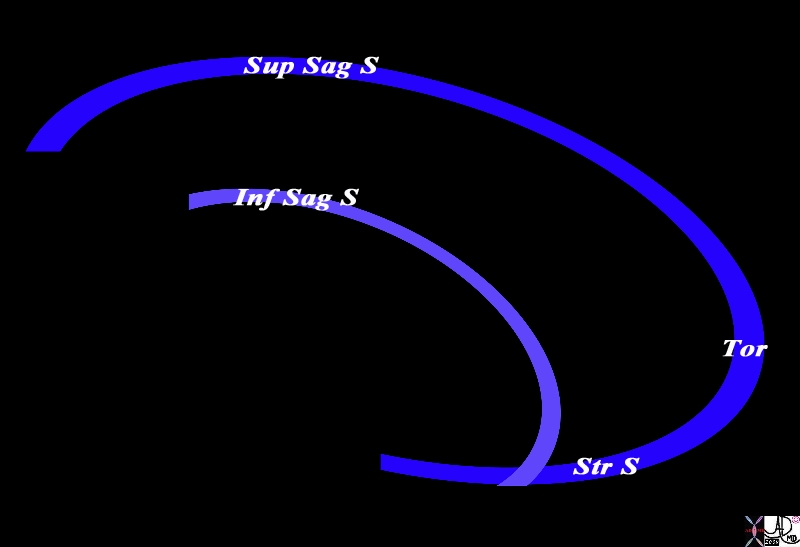
The conceptual framework for the venous drainage of the brain in the sagittal plane consists of two “inverted c’s”; The superior c (royal blue) represents the superior sagittal sinus (Sup Sag S) and its posterior end (bottom part of the “c” represents the straight sinus (Str S). The lower “inverted c” (light purple) represents the inferior sagittal sinus (Inf Sag S) and it joins the straight sinus to empty into the torcular herophili(Tor). co Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 98057d03.8sL |
The Horizantal “C” – Transverse Sinus and The Sigmoid Sinus |
|
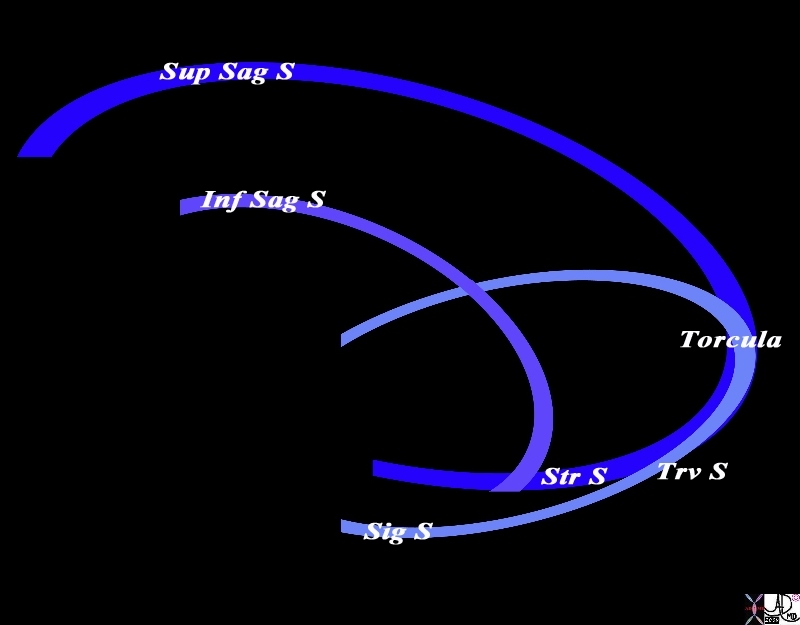
The conceptual framework for the venous drainage of the brain in the sagittal plane consists of two “inverted c’s”; The superior c (royal blue) represents the superior sagittal sinus (Sup Sag S) and its posterior end (bottom part of the “c” represents the straight sinus (Str S). The lower “inverted c” (light purple) represents the inferior sagittal sinus (Inf Sag S) and it joins the straight sinus to empty into the torcular herophili(Tor). The second component is a horizontal “C” (light blue) which represents the transverse sinus. (Trv S) which Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 98057d04b.8sL |
The Internal Jugular Veins Exit from the Brain |
|
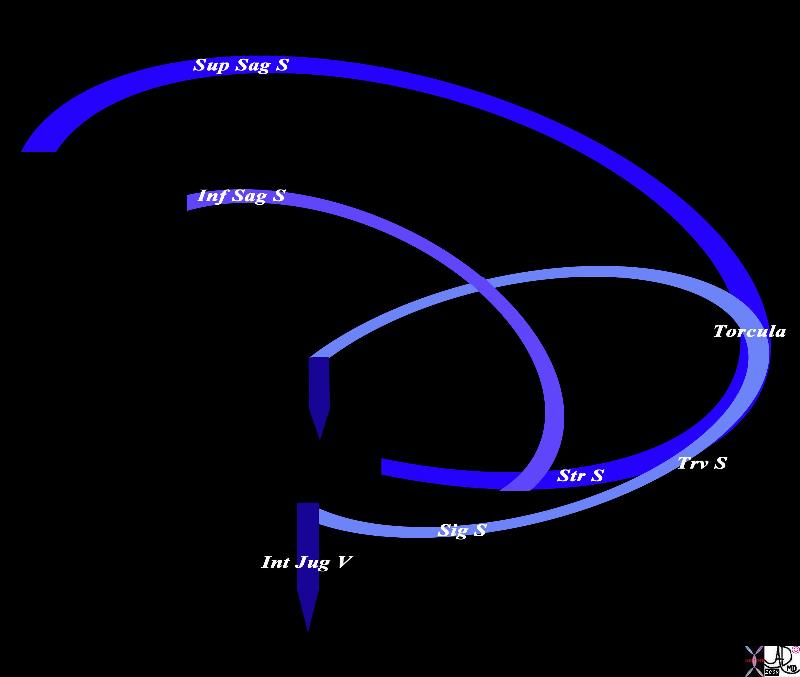
The conceptual framework for the venous drainage of the brain in the sagittal plane consists of two “inverted c’s”; The superior c (royal blue) represents the superior sagittal sinus (Sup Sag S) and its posterior end (bottom part of the “c” represents the straight sinus (Str S). The lower “inverted c” (light purple) represents the inferior sagittal sinus (Inf Sag S) and it joins the straight sinus to empty into the torcular herophili (Tor). The second component is a horizontal “C” (light blue) which represents the transverse sinus. (Trv S) which empties into the sigmoid sinus (Sig S). The horizontal ‘C” and the vertical ‘c’s” meet at the confluens called the torcular herophili (torcular) The final exit from the brain is via the right and left vertical internal jugular veins (navy blue – int J V) Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 98057d06.8S |
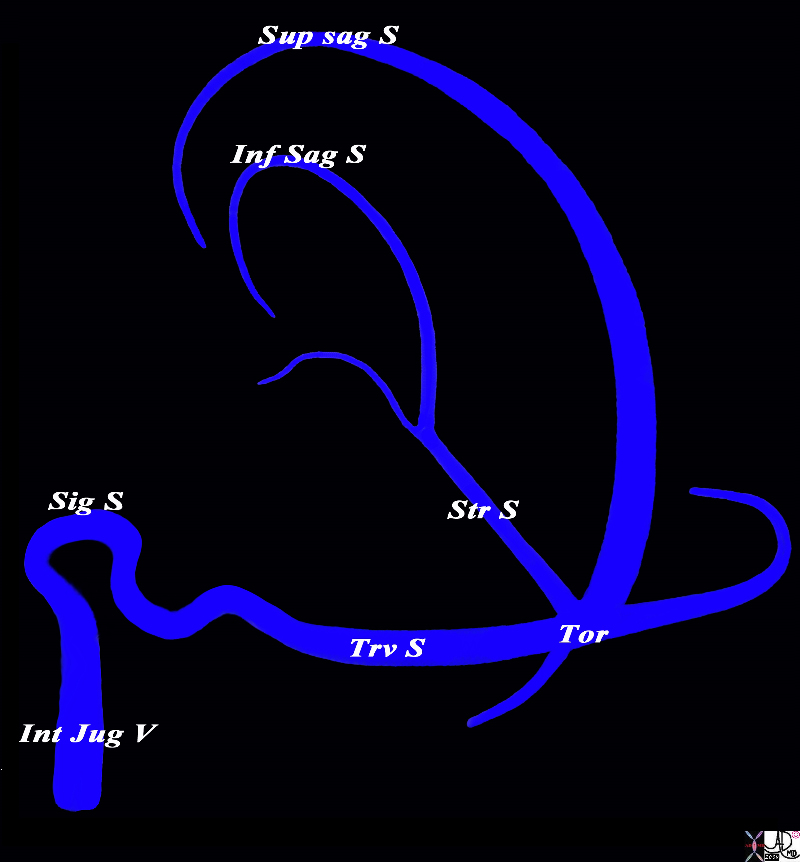
The Major Sinuses |
|
The diagram shows the basic plan of the dural sinuses and venous drainage of the brain in the parasagittal plane The superior sagittal sinus runs on the superior aspect of the falx and abuts the vertex of the skull. It usually empties into the right transverse sinus. The inferior sagittal sinus runs on the inferior aspect of the falx and empties into the straight sinus which in turn tends to empty into the left transverse sinus The transverse sinuses in turn empty into the sigmoid sinuses which exit the skull to enter the internal jugular veins. The confluence of the veins near the internal occipital protuberance is called the torcular heophili. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 98057d01L018s |