The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
Acute brain ishemia takes two main clinical forms;
Cerebrovascular accident (Stroke)
Transient Ischemic Attack
Cerebrovascular accident (CVA), or stroke, is a complex neurological syndrome circulatory in origin caused by acute changes in either local or global brain function as a result dysfunction of cerebral blood flow from thrombosis, embolism, or cerebral hemorrhage with symptoms lasting more than 24 hours. About 85% of strokes are ischemic and 15% due to cerebral hemorrhage.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA), is sudden loss of brain function for less than 24 hours due to embolism or vascular thrombosis and is part of the same spectrum of disorders.
Structurally the thrombosis and hemorrhage tends to be unoifocal, while embolic disease is multifical.
Functionally the brain is unable to tolerate hypoxia nor the secodary effects of hypoxia including inefficient enzymatic processes which result in excess sodium and calcium entering the cell and causing cell edema and apoptosis. The brain requires constant delivery of glucose and oxygen. Normal fblood flow is approximately 65 mL/min/ 100grs of tissue. When the flow is reduced to less than 25, and if circulation is restablishe then function can be restored. If however flow is reduced to less than 10 to 12mL/min/ 100grs of tissue, then irreversible changes result.
Clinically, the patient presents with focal sensory or motor deficits. Disorders of the carotid circulation more commonly results in deficits in language (aphasia) or with motor deficits more commonly of the face and upper limbs. Aphasia is usually caused a focal abnormality in the left hemisphere which is commonly dominant for language. When involvement is in the vertebrobasilar system, symptoms are more commonly of cerebellar motor dysfunction, including ataxia, or with cranial nerve motor dysfunction, such as dysphagia dysphagia, or dysarthria.
The diagnosis is based on the clinical presentation and on imaging. CT provides an early capability of quickly establishing the presence of hemorhagic change and thus provides a direction for therapy. Howevere it is not sensitive to the early changes of non hemorrhagic stroke which requires MRI for documentation.
In the hyperacute phase, CT may show hyperdensity of the middle cerebral artery. Within about 3 hours of onset CT may show hypodense changes if the stroke is large. After 5-6 hours the chance of visualising a non hemorrhagic stroke increases.
MRI is more sensitive to the early changes of stroke particularly if diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) sequence is employed. T2 weighted sequences and FLAIR are helpful as well.
Treatment with anticoagulation is optimised if used early in the process as long as hemorrhagic infarction is excluded.
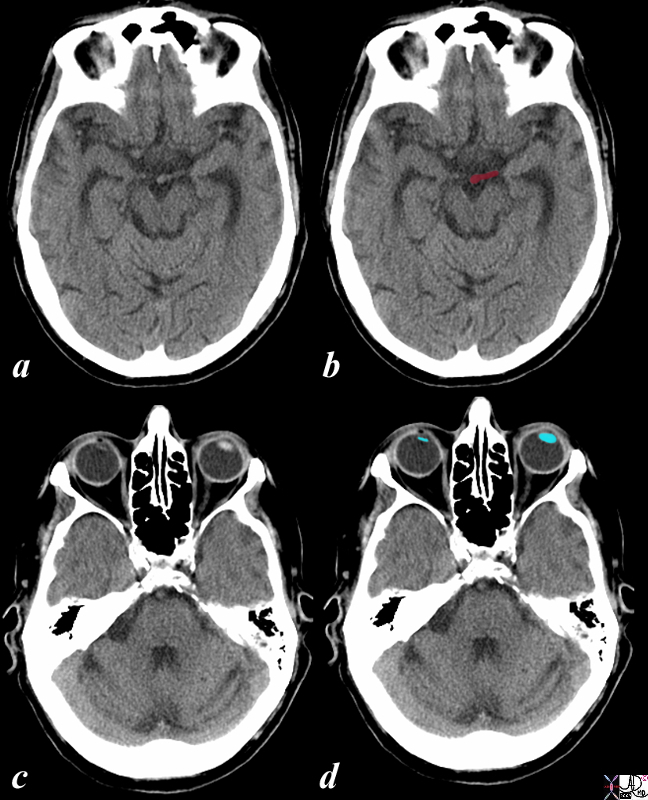
Acute Stroke Conjugate GAze and dense Left MCA |
|
The CT is from a 86year old male with an acute right sided stroke. The CT shows a dense left middle cerebral artery (LMCA) (maroon overlay in b) associated with deviation of the eyes (lenses overlaid in blue in d) to the side of the lesion and away from the side of the clinical weakness. (Prevosts sign) and is commonly associated with spatial neglect. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 98535c.8s |
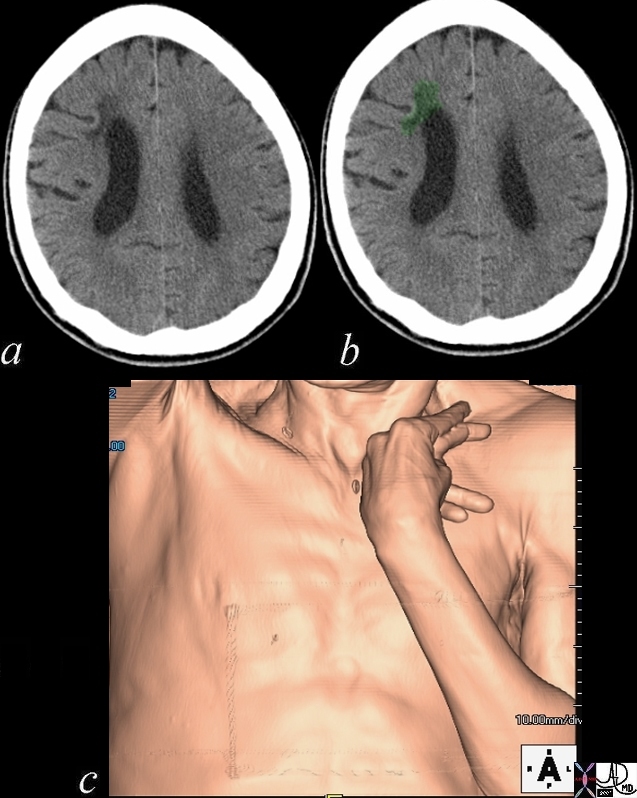
Hypertonoicty Due to a Chronic Stroke |
|
60 year old malewith The classical appearance of hypertonia of upper limb and hand muscles is shown in this CT volume rendered image. The hand and elbow are flexed as a result of involvement on the contralateral motor cortex. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD 48641c01.800 |
end
References
