The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Introduction
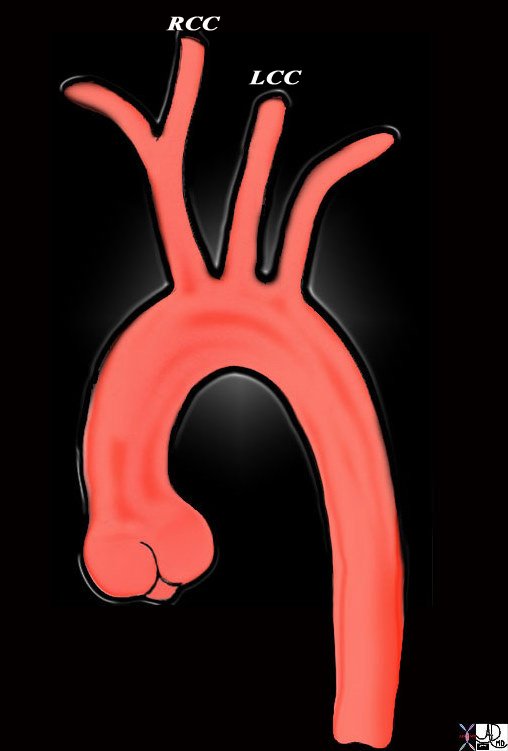
The carotid system arises from the aorta and consists of a right and left vessel. the right usually arises fromn the innominate artery or brachiocephalic artery which is the normally the first vessel off the aortic arch. The left common carotid arises as a single vessel off the arch as the second branch after the innominate artery
 Origins of the Carotid System Origins of the Carotid System
Things on the right and the left are not all equal |
|
This diagram shows the origin of the head neck and arm vessels from the arch of the aorta. The first vessel off the arch is the brachiocephalic or innominate artery and it branches into the right common carotid (RCC) and right subclavian artery. The second vessel is the left common carotid artery (LCC) and this is followed by the left subclavian artery. The RCC and LCC divide in the neck into the external and internal carotid vessels. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 All rights reserved 47676b |
The Internal Carotid
The internal supplies the anterior portion of the brain. The internal carotid arises from the common carotid artery. The posterior supply is provided by the verterbral arteries. The verterbral arteries are responsible for supplying most of the brainstem, cerebellum, spinal cord, parts of the temporal lobe and the occipital lobes. The internal carotid artery system supplies the rest of the brain. The internal carotid artery arises into the skull through the foramen lacerum and then runs anteriorly in the cavernous sinus until it makes a sharp turn to exit the sinus into the subarachnoid space. The internal carotid artery then gives rise to the posterior communicating artery and the anterior choroidal artery and then it bifurcates into the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. The anterior choroidal artery is a thin artery which supplies the choroid plexus, the optic tract, and parts of the internal capsule, and thalamus. The internal carotid also gives rise to the ophthalmic artery. The posterior communicating artery provides a communication between the anterior circulation and posterior circulation as it connects to the posterior cerebral artery, which is arises from the vertebral artery. The anterior cerebral artery runs between the longitudinal fissure and supplies the medial portion of the parietal and frontal lobes. The anterior communicating artery serves to connect the two anterior cerebral arteries within the longitudinal fissure. The middle cerebral artery runs into the Sylvian fissure. In its course the MCA gives rise to small branches which penetrate and supply deep structures within the brain. These branches are referred to as lenticulostriate arteries. Small branches off the MCA also supply the insula. The territory supplied by the MCA is vast, as in addition to those structures mentioned, it supplies a major portion of the lateral cerebral hemispheres.
External Carotid
 Carotid Artery Carotid Artery |
| The angiogram of the carotid artery in the neck in the lateral projection shows the common carotid vessel dividing into a more posterior internal carotid and a more anterior external carotid artery49400 Courtesy Ram Chavalli MD |
 The Internal Carotid System The Internal Carotid System |
|
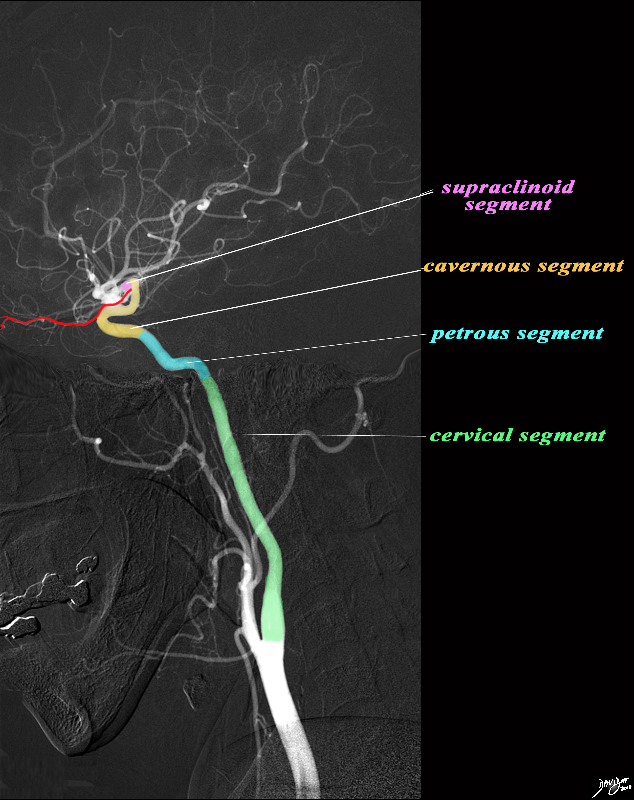
The angiogram demonstrates the carotid system in the lateral projection. The common carotid artery bifurcates in the base of the neck into the external and internal carotid artery. Basically the internal carotid artery supplies the brain and the external supplies the structures of the face and muscles and skin of the cranium. The internal carotid artery is divided into segments. The cervical segment (green) extends from the bifurcation to the base of the skull. The petrous segment (teal blue extends from the base of the skull to the apex of the petrous bone and enters the cranial vault via the foramen lacerum. The cavernous segment (light orange) passes through the cavernous sinus and exits by penetrating the dura. The ophthalmic artery (red) originates at the junction of the cavernous and supraclinoid segment. The supraclinoid segment materializes when the cavernous portion leave the dura. After a short distance it terminates by bifurcating into the middle and anterior cerebral arteries. Image courtesy Ram Chavalli MD Copyright 2010 49400bg.8s |
 Intracerebral Internal Carotid Branches – End of the Line before Final Bifurcation – A-P projection Intracerebral Internal Carotid Branches – End of the Line before Final Bifurcation – A-P projection |
| The angiogram is a from a 49 year old female who presented with headaches.The intracerebral angiogram shows the normal appearance in the A-P projection of the anterior and middle cerebral territory. The supraclinoid portion of the teminal portion of the internal carotid artery divides into the anterior cerebral artery that courses medially and the middle cerebral artery that branches laterally.
49422 Courtesy Ram Chavalli MD |
The internal carotid artery arises from the carotid bifurcation (at the level of vertebra C4), running through the anterior edge of the sternocleidomastoid. In the maxillo-pharyngeal space it ascends anteriorly and internally to the internal jugular vein. This is the C1 segment.
It accesses the base of the skull through the carotid canal, anteriorly to the jugular foramen – C2 segment. Thus, it will enter the petrous portion of the temporal bone while in the carotid canal, being accompanied by a sympathetic plexus from the cervical chain. This segment has a:
Vertical/Ascending segment anteriorly and internally to the timpanic cavity.
Genu segment in the axis of the petrous portion (curvature)
Horizontal segment that enters the cavernous sinus above the foramen lacerum
The C3 segment is a short segment that begins above the foramen lacerum, ending at the petrolingual ligament.
From here and until it perforates the dura – the C4 segment – describes a siphon and enters the cavernous sinus, and crosses laterally the posterior and anterior clinoid processes.In this segment, the artery is surrounded by nerves of the sympathetic trunk and the abducent nerve
It thus becomes intradural, until it enters the subarachnoid space – this short segment is called the C5 segment. As it gets into the subarachnoid space – C6 segment – it gives its main collateral – the ophthalmic artery.
Finally, C7 segment is when it passes between nerves II and III and the anterior perforated substance. It provides four terminal branches – the cerebral arteries:
anterior cerebral artery
middle cerebral artery
anterior choroidal artery
posterior communicating artery
Applied Biology
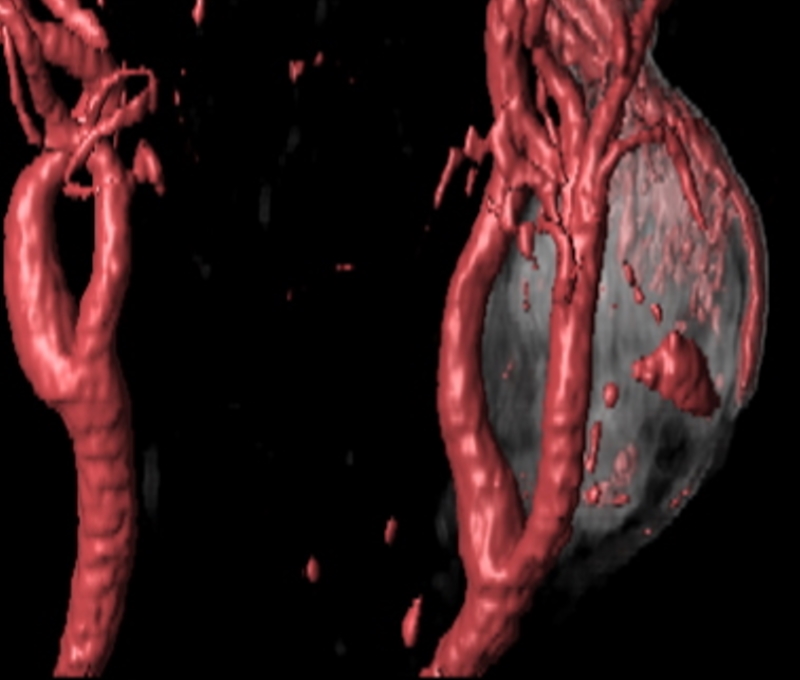 Carotid Body Tumor at the Carotid Bifurcation Carotid Body Tumor at the Carotid Bifurcation |
|
The CTA with volume rendering shows a mass (gray) at the bifurcation of the left common carotid. This location is classical for a carotid body tumor – or chemodactoma Philips Medical Systems 92506.8 |
