Cingulate Cortex
Copyright 2008
Definition
The cingulate cortex is part of the cingulate gyrus which is structurally characterized by its position above and parallel to the corpus callosum . Functionally it receives inputs from the anterior nucleus of the thalamus and from somatosensory cortex and is an integral part of the limbic system and is involved in learning, memory and emotion.
 Conceptual Diagram Conceptual Diagram
Cingulate Cortex Part of the Circle |
|
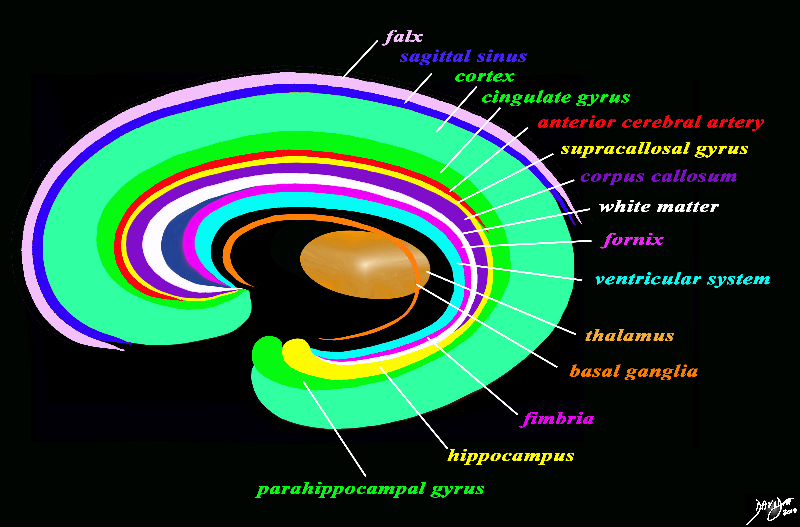
The forebrain has most of its components aligned in a series of inverted c- shaped rings starting from the outer membranes that culminate in the falx (pink), then extending inward smaller inner rings with each intimately connected to the others. The thalamus (dull orange) appears diagrammatically as the centre of these rings as seen from the sagittal view The outer ring is the falx (pink) followed by the sagittal sinus (blue) cerebral cortex (light green), cingulate gyrus (bright green) superiorly which becomes the parahippocampal gyrus inferiorly. The red ring represents the distribution of the main portion of the anterior cerebral artery. Next is the yellow ring which is the supracollosal gyrus (indusium griseum) superiorly and the hippocampus inferiorly. This is followed by the corpus callosum (purple) which enables the white ring of white matter to connect between hemispheres. The next ring is the thin bright pink ring which represents the fornix superiorly and the fimbria inferiorly. The innermost ring (light blue) represents the lateral horns of the ventricular system. The basal ganglia run just lateral to the lateral ventricles. The navy blue arrow headed structure is the septum pellucidum. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff copyright 2010 all rights reserved 93907d13g03.8s |
 The Cingulate Cortex (Gyrus) An Independant Lobe of the Forebrain The Cingulate Cortex (Gyrus) An Independant Lobe of the Forebrain
Part of the Limbic System |
|
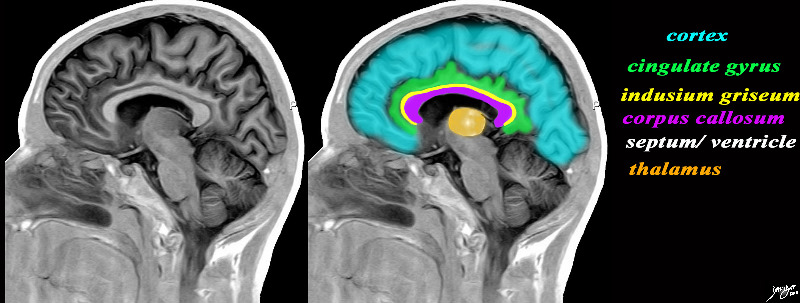
The sagital view of the brain reflects some of the inverted c-shaped rings including the cortex, cingulate gyrus, indusium griseum, corpus callosum, septum pellucidum/lateral ventricles, and the thalamus which is central. The cingulate gyrus (cortex crosses the boundaries of the frontal parietal and occibital lobes and is in close aasociation with other “inner circle” structures including the thalamus and corpus callosum for example. Image Courtesy of Philips Medical Systems Image Rendered by Davidoff 92170c01b01b01.8s |
T2 Weighted Image in the Sagittal Plane |
|
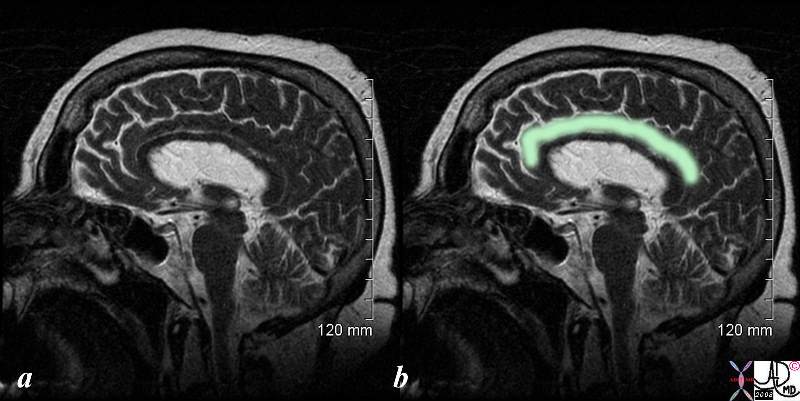
Cingulate means a belt or a ridge The MRI image in the midsagittal plane shows the T2 characteristics of the cingulate cortex – gray and white matter “fused” and isointense similar to the gray and white matter of the visualized components of the forebrain Cingulate gyrus (belt ridge in eng.) lies in the medial part of the brain and partially wraps around corpus callosum above is cingulate sulcus> Fnctionally it receives inputs from the anterior nucleus of the thalamus and from somatosensory cortex integral and is part of the limbic system, and is involved in learning, memory and emotion. Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 71430c02.8s |
 The Cingul;ate Gyrus and the Limbic System The Cingul;ate Gyrus and the Limbic System |
|
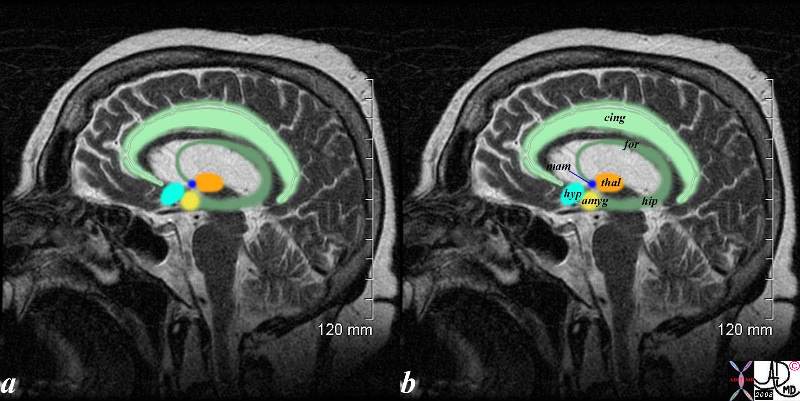
The sagittal T2 weighted shows the limbic system which is a compound set of structures including the cingulate gyrus, (light green) cingulate cortex, hypothalamus (light blue) mamillary body (royal blue) fornix (darker green) hippocampus (darker green) amygdala (yellow) and thalamus (orange). Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD copyright 2008 71430.85c01s |
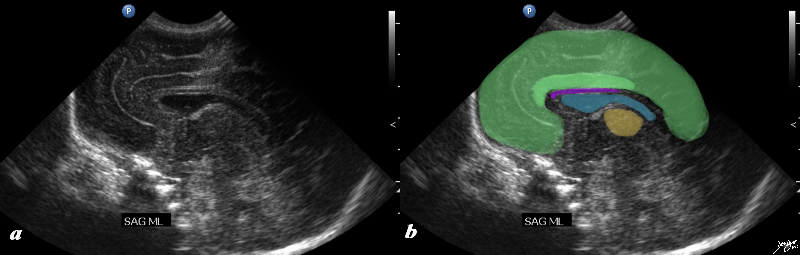 Ultrasound of Cingiulate Cortex in a Neonate Ultrasound of Cingiulate Cortex in a Neonate |
|
The ultrasound of a 7 day old baby boy reveals a normal sagittal section through the brain showing the CSF filled lateral ventricle (light blue) with most the brain substance showing characteristic homogeneous solid organ texture. The echogenic interfaces of the sulci with the gyri enable the outline of characteristic forms of the gyri so that for example the cingulate gyrus (darker green) is easily recognized by its classical location above the corpus callosum (purple). The corpus callosum is hypoechoic and overlaid in purple. The thalamus is isoechoic (orange) recognized by its position and shape rather than any unique ultrasound characteristics. The forebrain including the frontal parietal and temporal lobes are overlaid in green Courtesy Ashley Davidoff MD Copyright 2010 90986c02.8s |
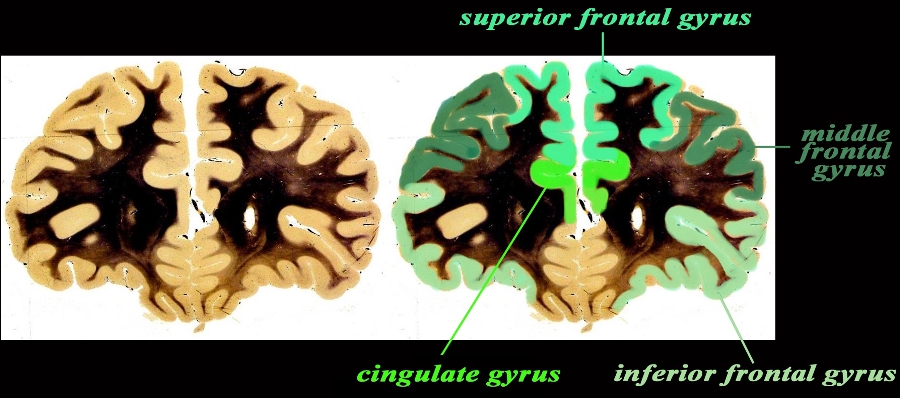 Cingulate Gyrus and Other Frontal Lobe Gyri Coronal Section Cingulate Gyrus and Other Frontal Lobe Gyri Coronal Section |
|
The coronal anatomical image is taken through the frontal lobe just at the extreme anterior portion of the frontal horns. The specimen shows the approximate position of the 3 major frontal gyri in the anterior location including the superior, middle and inferior gyrus. The cingulate gyrus is not really part of the forebrain but part of the limbic system. It holds a medial deep and very central position. Courtesy Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology at Boston University School of Medicine Dr. Jennifer Luebke , and Dr. Douglas Rosene Overlays Ashley Davidoff MD 97340.C1.gc01L2.9 |
