Meningioma
The Common Vein Copyright 2010
Definition
A meningioma is the most common extraaxial tumor characterized as a neoplasm originating from the arachnoid cap cells.
There are various contributing etiologic factors including trauma, radiation, and viral. Inherited causes are also seen, including hereditary meningiomas and neurofibromatosis type II.
Meningiomas can occur at any location where there is arachnoid tissue, commonly seen along the parasagittal dura, at the convexities, involving the sphenoid wing and at the cerebello-ar pontine angle cistern among others. Meningiomas can also be located within the ventricles where they arise from arachnoid cell rests within the choroid plexus. Depending on their location, meningiomas can lead to a variety of symptoms or be a completely incidental finding.
Imaging includes the use of CT however MRI is better for evaluating true extent of the lesion and vascular or sinus involvement as well as improved soft tissue contrast for evaluation of the adjacent brain parenchyma. On CT, over half of meningiomas are hyperdense, and they may occasionally contain calcification. CT may also demonstrate hyperostosis in the bone adjacent to the tumor. On MRI, these masses are typically isointense to hypointense on T1 and isointense to hyperintense on T2. Avid enhancement is seen after contrast administration. The dural tail sign is increased enhancement of the dura adjacent to the mass which is suggestive of a meningioma. Meningiomas also have a classic finding on conventional angiography known as the “mother-in-law” sign where contrast shows up early (in the arterial phase) and leaves late (with persistent venous staining).
Treatment options include surgery, radiation, radiosurgery, or conservative management with serial exams.
|
Meningioma MRI and CTscan |
|
On this posterior view f the brain the cerebellum and posterior part of the hemispheres are seen separated by the interhemispheric fissure This series of MRI and CT shows a large mass in the right frontal region (T1 C-) that displaces the falx across the midline and compresses and ablates the anterior horns of the right and left lateral ventricles. It enhances homogeneously (T1C+) and is heterogeneous and mostly hypointense on the T2 weighted image, and almost isodense and barely visible on the narrowed windows of the non contrast CT (CTC-) Edema of the surrounding compressed brain is seen on the T2 weighted image posterior to the tumor. This lesion was a meningiomas Image Courtesy of James Donnelly MD 23081c.8s |
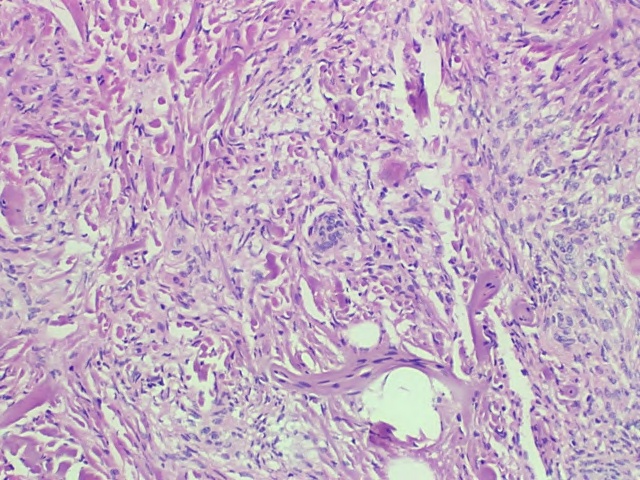
H&E Low Power This low power polymicrograph demonstrates finding consistent meningioma with pink areas of dural collagen which percolates through the tumor cells. There is a “whorled” area of tumor cells in the center of the image which is classic for meningioma. Overall, the cells are monomorphous, consistent with the benign character of this lesion.
Immunohistochemical staining for MIB-1 Meningioma |
|
Immunohistochemical staining for MIB-1 which assesses the rate of tumor cell proliferation rate demonstrates few positively staining nuclei. Images Courtesy of Cheryl Spencer, M.A. and Ivana Delalle, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Boston University School of Medicine 98511/12 |
AFIP
Requisites
Robbins